Inspirational journeys
Follow the stories of academics and their research expeditions
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVDs)
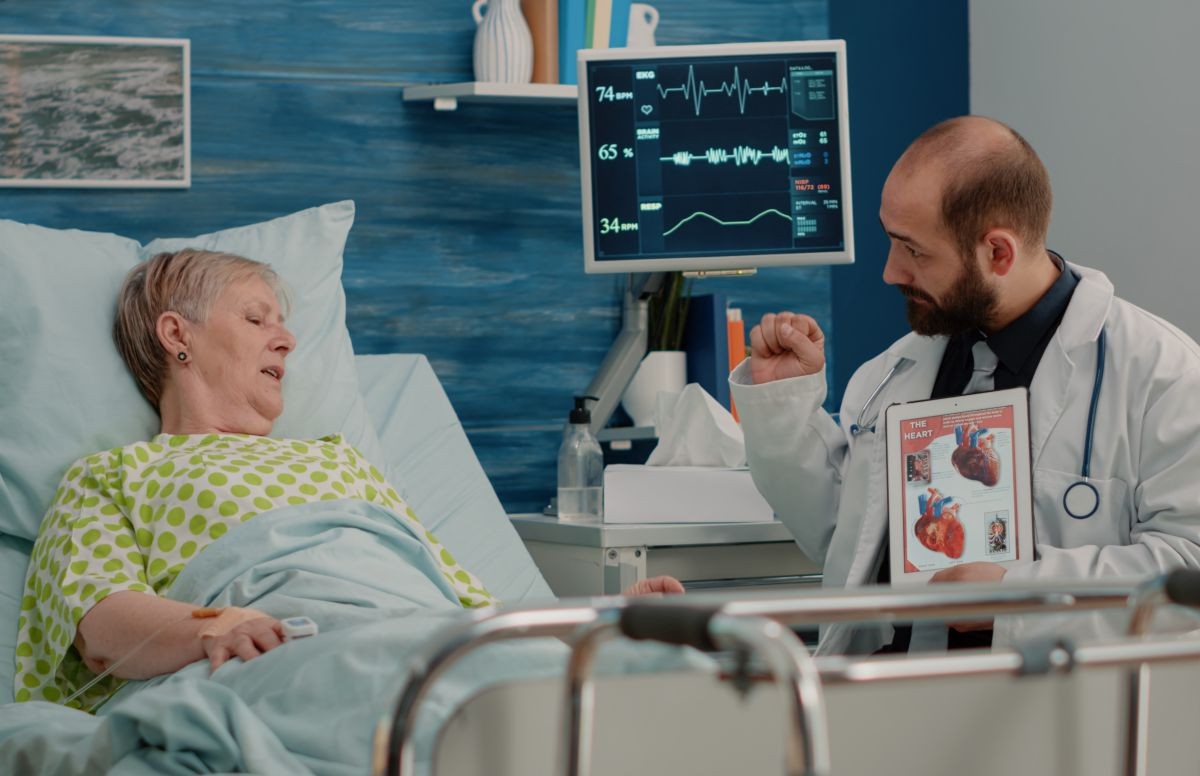

Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) include conditions that affect the blood vessels of the heart, coronary heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, and other conditions that affect the heart.
The burden of CVDs – A matter of
concern
CVDs are the leading cause of mortality
globally, claiming the lives of an estimated 17.9 million people every year.
More than four out of every five CVD deaths are caused by heart attacks and
strokes, with one-third of these deaths occurring before the age of 70.
Abnormal heart rhythms (or arrhythmias),
Aorta disease and Marfan syndrome, Congenital heart disease, Coronary artery
disease (narrowing of the arteries), Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary
embolism, Heart attack, Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy), Heart valve
disease, Pericardial disease, Peripheral vascular disease, Rheumatic heart
disease, Stroke, and Vascular disease are all examples of CVD (blood vessel disease).
Cardinal signs and symptoms of
cardiovascular disease include:
o
Chest pain or pressure, which could indicate angina.
o Pain
or discomfort in the left shoulder, radiating pain to the arm, elbows, jaw, or
back
o
Nausea and exhaustion
o
Excessive gasping for air
o
Feeling light-headed or dizzy
o
Excessive sweating
Risk
Factors for the development of cardiovascular disease
o Behavioral risk factors: Some
of the most important behavioral risk factors for CVD include
1. Tobacco use
2. An unhealthy diet
3. Excessive alcohol consumption
4. Inadequate
physical activity
o Physiological factors: These
factors are linked to underlying social determinants and drivers such as age,
income, and urbanization.
1.
High blood pressure (hypertension)
2. High blood cholesterol
3. High blood sugar
or glucose,
Tips to reduce the risk of CVD
Tobacco cessation, salt reduction in the
diet, increased fruit and vegetable consumption, regular physical activity, and
avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption have all been shown to reduce the
risk of cardiovascular disease.
Identifying those who are most at risk
for CVDs and ensuring that they receive appropriate treatment can help to
prevent premature deaths. To ensure that those in need receive treatment and
counseling, all primary health care facilities must have access to
non-communicable disease medicines and basic health technologies.
Management of CVD
The treatment options for cardiovascular
diseases vary depending on the condition and may include
o
Lifestyle
modification: Altering aspects of your lifestyle, such as your diet,
exercise, and alcohol and tobacco use.
o
Medications,
such as those used to treat risk factors such as high blood pressure or
cholesterol, or to dissolve clots.
o
Medical
procedures/Interventions such as putting a balloon or stent
in your artery, heart valve surgery, or coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
0 Comments
Categories
Recent posts
IQAI: Transforming Healthcare - One Success Story at a Time
Wed, 20 Sep 2023




Leave a comment