Inspirational journeys
Follow the stories of academics and their research expeditions
CEREBRAL PALSY : Symptoms, Causes, & Types.
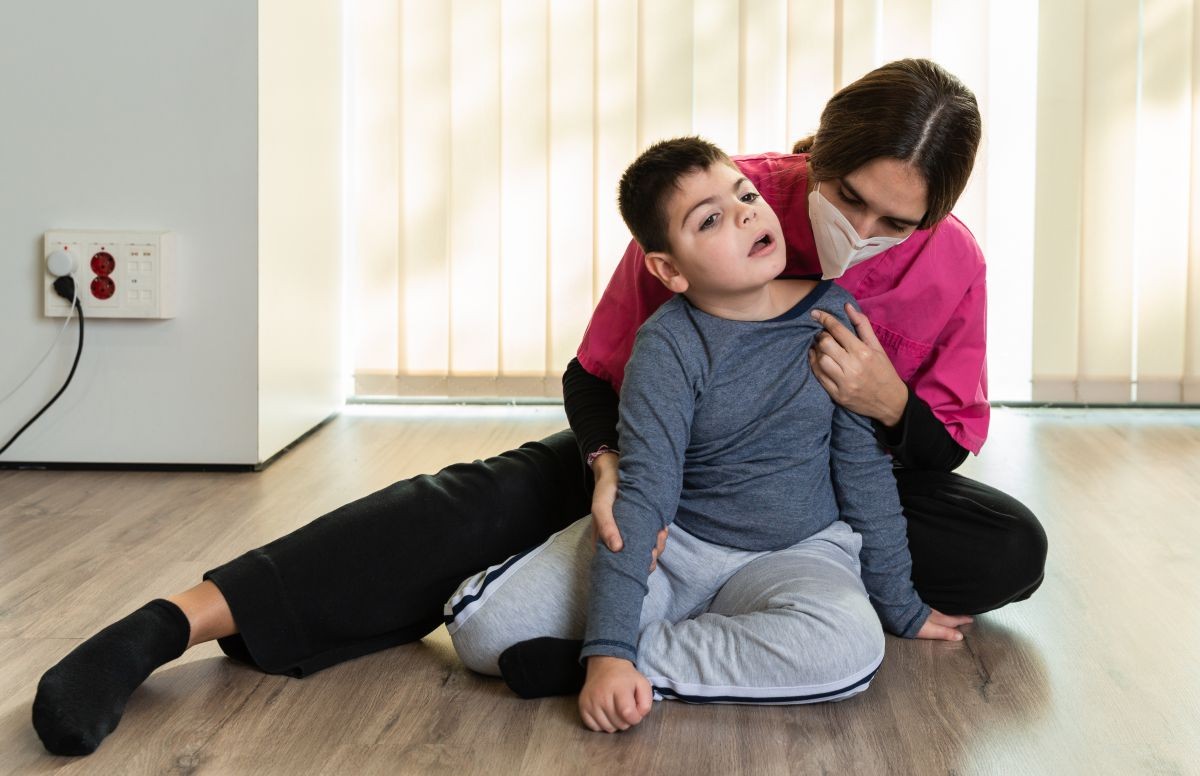

Cerebral palsy affects approximately 17 million people
worldwide. Childhood CP is the most common motor disability. CP affects
approximately 1 in every 345 children. It has been discovered that 10% of the
global population suffers from some form of disability, with India accounting
for 3.8 percent of the population. Cerebral Palsy affects approximately 15-20%
of physically disabled children. In India, the incidence is estimated to be
around 3/1000 live births.
In Uganda, cerebral palsy is more common and has a higher
mortality rate than in high-income countries. Cerebral malaria is most likely
to blame for the underlying brain injury that occurs during early childhood.
Cerebral palsy is on the rise among blacks, owing to higher rates of low birth
weight.Cerebral palsy (CP) is a problem
that affects muscle tone, movement, and coordination. It happens when the brain
can’t properly send messages to muscles about how to move in smooth or
well-coordinated ways. It can also affect other body functions that involve
motor skills and muscles, like breathing, bladder and bowel control, eating,
and talking.
Sometimes
the cause of CP is unknown. Many cases, however, occur while a child's brain is
still developing, such as before birth or during early childhood. This could be
cause by:
· Infections or other medical issues during pregnancy
· A stroke in the womb or after birth
· Untreated jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the
eyes)
· Genetic disorders
Premature babies
(babies born early) have a higher risk of developing CP than full-term babies.
Low-birth-weight babies and multiple births, such as twins and triplets, have
similar risks. Lead poisoning, bacterial meningitis, poor blood flow to the
brain, being shaken as an infant (shaken baby syndrome), and an accident injury
can all cause brain damage (like a car accident).
How to diagnosed Cerebral Palsy?
·
Delays
in development, such as not reaching for toys until 4 months or not sitting up
until 7 months.
·
Issues with motor skills, such as
inability to crawl, walk, or move arms and legs normally.
·
Inconsistent movements
·
Excessively tight or excessively
loose muscle tone
·
Infant reflexes (such as the palmar
grasp, or "hands in fists" reflex) that last longer than they should.
With CP, a variety of physical issues can arise. Some
children struggle with movement, while others do not. It depends on the extent
of the brain damage. Damage can be partial, affecting only the part of the
brain that controls walking, for example. It can also affect a larger area, such
as the parts of the brain that control walking, talking, and comprehension. The
brain damage that causes CP can also affect other brain functions, resulting in
issues such as:
·
Blindness or visual impairment
·
Food aspiration (the inhalation of
food or liquid)
·
Gastro-esophageal
reflux (spitting up)
·
Sleep disorders
·
Speech problems and/or drooling
·
Osteoporosis is a disease that
affects the bones (weak, brittle bones)
·
Seizures
·
Issues with behavior
Although there is no cure for CP, a child's quality of life
can be improved with:
·
Treatment that may involve medicine
or surgery.
·
Therapy, including physical therapy,
occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
·
Special equipment to help kids get
around and communicate with others.
·
Kids can improve their bone health
by having a diet that's high in calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus.
While
there is no way to completely prevent CP, there are some things that can be
done to reduce the chances of a child developing it:
•
Avoiding
infections or viruses that can harm the fetus, such as rubella or zika, during
pregnancy.
•
Getting
a rubella vaccination before trying to conceive.
•
Managing
underlying health issues like blood pressure, diabetes, and so on.
•
Identifying
any potential Rh factor incompatibility between mother and child during
pregnancy.
•
Proper
medical care during delivery.
•
Reducing
the risk of head injury during/after birth.
0 Comments
Categories
Recent posts
IQAI: Transforming Healthcare - One Success Story at a Time
Wed, 20 Sep 2023




Leave a comment