Inspirational journeys
Follow the stories of academics and their research expeditions
Hemoptysis- What it is, Causes & Treatment
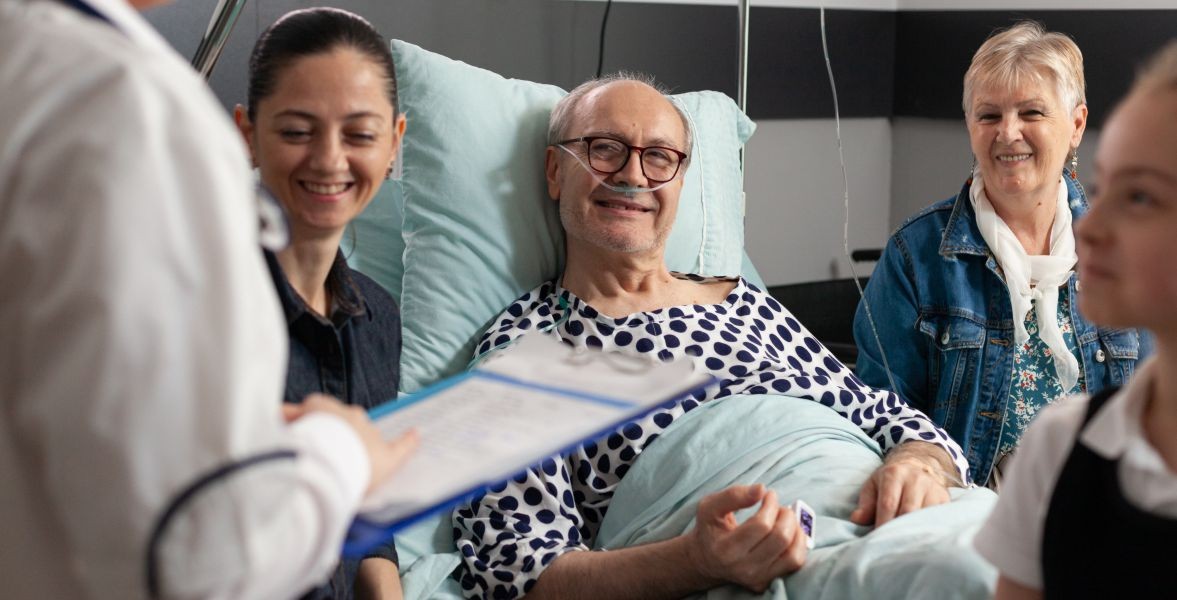

Hemoptysis
is the coughing /spitting up of blood from the respiratory tract. It's
unremarkably caused by pneumonia, bronchiectasis, bronchitis, and carcinoma.
The expectorated blood sometimes originates from the vessels. Once hemoptysis
is observed then it should be classified based on severity, and the origin and
reason behind the hemoptysis is determined. Lateral and AP chest X-ray is the
initial study, though a standard chest X-ray doesn't rule out the chance of
malignancy or any underlying pathology.
Multidetector
CT (MDCT) should be performed in patients with frank hemoptysis, suspicion of
bronchiectasis or associated risk factors for carcinoma, and in those with
signs of pathology on chest X-ray.
MDCT
may be a non-invasive imaging technique that
will pinpoint the presence, origin, variety, and source of the general
(bronchial and non-bronchial) and pneumonic blood vessel sources of bleeding.
Endovascular embolization is the safest and simplest methodology for managing bleeding
in severe hemoptysis.
Flexible
bronchoscopy plays a crucial role in the diagnosing of hemoptysis in patients
with frank hemoptysis. The procedure is performed in the intensive care unit;
it is used for immediate management of bleeding and is additionally effective
in locating the source of the hemorrhage.
Causes
of hemoptysis -
There
is a broad medical diagnosis for hemoptysis, associated with infections, tracheal
involvement, malignancy, and foreign body aspiration or trauma. In developing
countries, one of the foremost common causes of hemoptysis is TB. However, in
developed countries, bacterial infection superimposed on chronic respiratory
sickness, like Cystic Fibrosis is also the cause. Acute infectious respiratory
disease, pneumonia; and other infectious agents, like Aspergillus, Nocardia,
and non-tuberculosis mycobacteria, may additionally be accountable.
Finally,
bleeding disorders, medicine use, foreign body aspiration, and respiratory
organ trauma can contribute to the etiology of hemoptysis.
Treatment
for hemoptysis –
Treatment
of hemoptysis depends on the underlying cause and severity. In large hemoptysis
or severe hemoptysis, securing the patient’s airway is a priority. Start on
Basic medical aid, intubated, or repositioned in the lateral attitude position
(i.e., on the affected side), which uses gravity to stop blood from getting
into the unaffected lung. Intravenous fluid and transfusion are also indicated.
Bronchoscopy to insert a balloon tube or embolize the artery to prevent further
bleeding can be used. In some circumstances, surgical intervention is also needed.
In
non-massive hemoptysis, management of the underlying cause is the first
treatment strategy. Infection is treated with antibiotics, antivirals, or
antifungals. Signs of malignancy might need a consultation with an oncologist.
Underlying chronic respiratory sickness is also treated with glucocorticoids,
bronchodilators, mucolytics, chest physiotherapy, or basic first aid. Studies
have additionally shown that inhalation of tranexamic acid (i.e.,
antifibrinolytic) in people with mild hemoptysis provides fast symptomatic
relief and shorter hospital stays.
0 Comments
Categories
Recent posts
IQAI: Transforming Healthcare - One Success Story at a Time
Wed, 20 Sep 2023




Leave a comment