Inspirational journeys
Follow the stories of academics and their research expeditions
Types of poison and their adverse effect
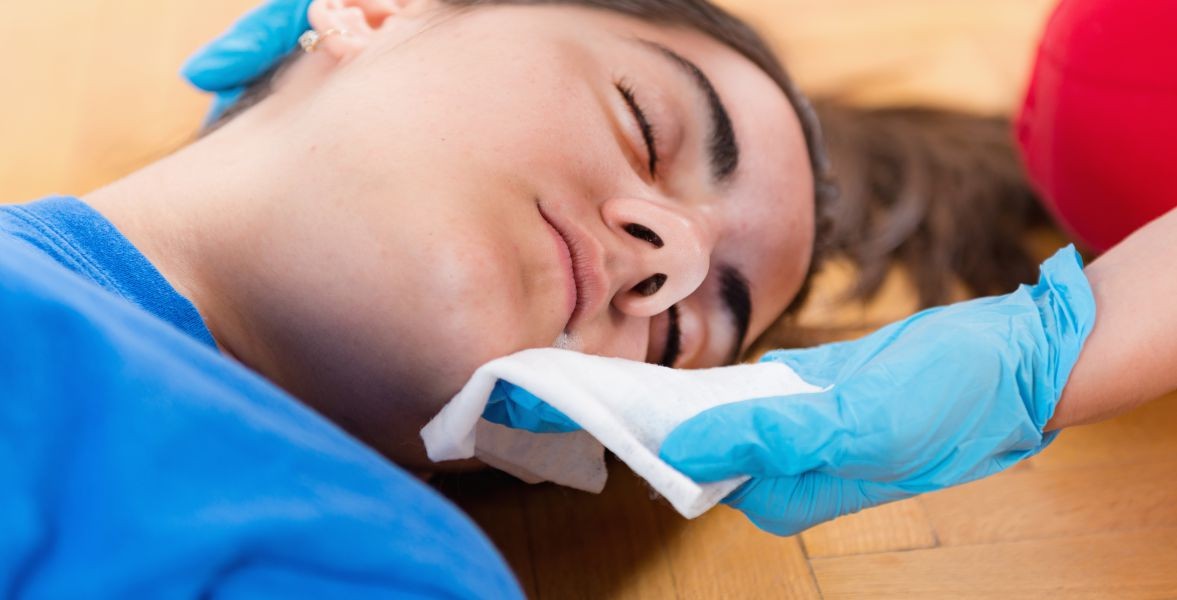

If the
person has no symptoms even though he/she may have consumed the poison, then it
is important to immediately reach the hospital or emergency room for poison
treatment
Poison is
something that kills or injures the cells/tissues through its chemical actions.
Most poisons are ingested. The word poison comes from the Latin word – “potare”
- assuming to drink. However, poisons can even enter the body in other ways:
- Through inhalation [spreads via respiratory]
- Through
the skin
- By
IV injection
- From
exposure to radiation
- Venom
from a snake bite
Poisons
embrace contact with extremely toxic chemicals not meant for human intake like
cyanide, paint thinners, or unit cleansing merchandise.
Many
substances that are meant for human consumption such as a few foods and
medicines, can be lethal if consumed in excess
Foods
·
Some
mushrooms are toxic
·
Drinking
contaminated water
·
Food
that has not been properly handled
·
Drugs
·
Drugs
that are useful in therapeutic doses could also be deadly if taken in excess.
Examples
include:
Drugs
Beta-blockers: Beta blockers are used
to treat heart conditions (for example, angina, and abnormal heart rhythms) and
other conditions, (for example, high pressure, sick headache bar, phobic
disorders) In excess, they can cause problems.
Warfarin (Coumadin): Anticoagulant is the
active ingredient in several rat poisons and could cause serious injury and
death if an excessive amount is taken.
Vitamins: Vitamins, particularly A and D, if
taken in large amounts can cause toxicity.
Signs and symptoms of poisoning are
variable and there is no simple way to classify them.
·
Enlarged/dilated pupils
·
Excessive drooling/Dry mouth and skin.
·
Some increase the respiratory rate, whereas
others may slow it.
·
Some are painless and few are painful
·
Some may cause loss of consciousness
0 Comments
Categories
Recent posts
IQAI: Transforming Healthcare - One Success Story at a Time
Wed, 20 Sep 2023




Leave a comment